Sử dụng biểu thức phụ để tìm cực trị của biểu thức
- Lý thuyết cơ bản chứng minh bất đẳng thức
- Lời khuyên bổ ích khi học bất đẳng thức
- Phương pháp biến đổi tương đương chứng minh bất đẳng thức
- Ứng dụng bất đẳng thức để giải phương trình
- Một số bất đẳng thức phụ hay dùng
- Chọn điểm rơi trong bất đẳng thức như nào?
- Chứng minh bất đẳng thức bằng phương pháp đổi biến
- Bất đẳng thức Schur với t=1. Các kết quả hay sử dụng
- Sử dụng biểu thức phụ để tìm cực trị của biểu thức
- Chứng minh bất đẳng thức bằng phương pháp ghép cặp
- Ứng dụng Cosi ngược dấu chứng minh bất đẳng thức
- Cách chứng minh bất đẳng thức bằng vectơ
- Bất đẳng thức Côsi (Cauchy) và bài tập áp dụng
- Bất đẳng thức Bunhiacopxki và các kỹ thuật thường dùng
- Tuyển tập một số bài toán bất đẳng thức trong kì thi chuyên Toán 2020
- Bất đẳng thức Svac-xơ (bất đẳng thức cộng mẫu số)
Khi tìm cực trị của biểu thức gặp khó khăn ta có thể nghĩ tới việc sử dụng biểu thức phụ, khi phân tích biểu thức phụ dễ hơn.
Cách làm như sau:
Để tìm cực trị của biểu thức
với, ta có thể xét cực trị của biểu thức:
(
là hằng số)
Xem các ví dụ dưới đây để hiểu thêm về cách sử dụng biểu thức phụ để tìm GTNN, GTLN.
Ví dụ 1: Tìm giá trị lớn nhất của ![]()
Giải :
a) Xét ![]() ⇒
⇒ ![]() giá trị này không phải là GTLN của
giá trị này không phải là GTLN của ![]() vì với
vì với ![]() ta có
ta có ![]()
b) Xét ![]() khi đó
khi đó ![]()
với cách đặt trên ta có: ![]()
Ta có:
![]() (theo Cô si)
(theo Cô si)
![]()
Do đó :![]()
Ví dụ 2: Tìm GTNN của ![]() với
với ![]()
![]()
Đặt ![]() như vậy
như vậy ![]()
Ta có ![]() vói
vói ![]()
Đặt ![]() vói
vói ![]() khi đó
khi đó ![]() Max
Max
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() do
do ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Vậy ![]()
Ví dụ 3: Tìm GTLN của ![]()
Giải:
Do ![]()
Đặt : ![]() khi đó
khi đó ![]()
Ta có : ![]()
![]() theo Bunhiacôpxki
theo Bunhiacôpxki
![]() do
do ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Vậy ![]()
Ví dụ 4: Cho ![]() . Tìm GTNN của
. Tìm GTNN của
![]()
Giải:
Đặt ![]() ta có :
ta có :
![]()
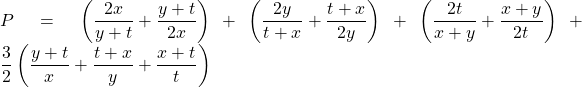
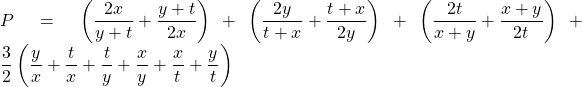
![]() (theo cô si)
(theo cô si)
![]()
![]()
Vậy ![]()
Ví dụ 5: Cho ![]() và
và ![]() .
.
Tìm GTLN của ![]()
Giải:
Đặt : ![]() ta có :
ta có :
![]() (theo Cô si)
(theo Cô si)
![]()
Dấu “=” xảy ra ![]()
![]()
Ví dụ 6: Cho ![]() , Tìm GTLN của
, Tìm GTLN của ![]()
Giải:
Xét : ![]() khi đó
khi đó ![]()
Đặt : ![]() khi đó
khi đó ![]()
Theo Bunhiacôpxky : ![]()
![]()
hoặc ![]()
![]()
Do ![]()
![]()
Vậy ![]()
Ví dụ 7: Cho ![]() Tìm GTNN của
Tìm GTNN của ![]()
Giải:
Đặt : ![]() ta có :
ta có :
![]()
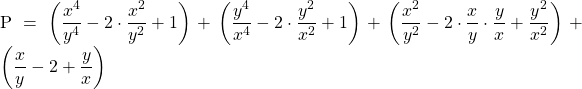
![]()
![]()
Vậy ![]()
Bài tập:
1. Cho ![]() và
và ![]()
Tìm GTNN của ![]()
2. Cho ![]() . Tìm GTNN của
. Tìm GTNN của ![]()
3. Cho ![]() . Tìm GTLN của
. Tìm GTLN của ![]()
4. Cho ![]() . Tìm GTLN của
. Tìm GTLN của ![]()
5. Cho ![]() và
và ![]() . Tìm GTNN của
. Tìm GTNN của ![]()
6. Cho a, b, ![]() . Tìm GTNN của:
. Tìm GTNN của:
![]()
7. Cho ![]() . Tìm GTNN của
. Tìm GTNN của ![]()
Các dạng bài tập giải bài toán bằng cách lập phương trình, hệ phương trình
Biện luận nghiệm của phương trình bậc 2 bằng đồ thị
Cách chứng minh bất đẳng thức trong đề thi vào 10 môn Toán
Ví dụ giải hệ phương trình quy về bậc nhất
Hệ phương trình bậc nhất chứa tham số
Hệ phương trình đối xứng loại 1, loại 2 có hai ẩn
Cách tìm hai số khi biết tổng và tích của chúng